PHP – MySQL
Connection and Data Access
12/26/2008
1. Data entry
<form action="handle_form.php" method="post">
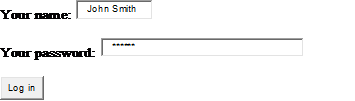
<p>Your name: <input type="text" name="myname" size="20" maxlength="40" /></p>
<p>Your password: <input type="password" name="mypassword" size="40" maxlength="60" /></p>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Log in" /></div>
</form>
2. Data processing
<?php // handle_form.php
if (!empty($_POST [ ‘myname’ ] ) )
{
$fm_username = $_POST [ ‘ myname’ ]; // $name ¬ “John Smith”
}
else
{
echo '<p class="error">You forgot to enter your name.</p>';
}
if (!empty($_POST [ ‘mypassword’ ] ) )
{
$fm_password = $_POST [ ‘mypassword’ ]; // $password ¬ “******”
}
else
{
echo '<p class="error">You forgot to enter your name.</p>';
}
3. Connect to the database (using an included file)
<?php
$host = ‘localhost’;
$user = ‘username’;
$passwd = ‘password’;
$dbnm = ‘database_name’;
$dbc = @mysqli_connect
($host, $user, $passwd,
$dbnm)
or exit ( ) ;
[
Or,
$dbc = mysqli_connect
( $host, $user, $pass )
or exit ( );
mysqli_select_dbnm ($db); ]
?>
4. Query MySQL to obtain data
$query = "SELECT username AS db_name, password AS db_pass FROM user_info" ;
$result = @mysqli_query ($dbc, $query) OR exit ( ' Could not execute the query." ) ;
$row = mysqli_fetch_assoc ($result);
$number_rows = mysqli_num_rows ($result);
extract ( $row ) ;
if ($result) { // or: if ($number_rows > 0)
for ($i=0; $i<$number_rows; $i++) {
if ($fm_username = = $db_name && SHA1($fm_password) = = $db_pass)
echo " <p>Wellcome $fm_username, you are now logged in </p>";
……
mysqli_free_result ( $result ) ; // Free up the resources.
mysqli_close($dbc);
}
}
}
Notes:
(1) $query is a MySQL
query statement;
When using quotes in a $query statement,
you are actually using quotes on two
levels: the quotes needed to assign the
string to variable $query and the
quotes that are part of the SQL language query itself. The use of double and single
quotes:
a. Use double quotes at the beginning
and end of the string.
b. Use single quotes before and after
variable names.
c. Use single quotes before and after
literal values. For example,
$query = “SELECT firstname
FROM member”;
$query = “SELECT firstname
FROM member WHERE lastname=’Smith’ ”;
$query = “UPDATE member SET lastname=’last_name’ ”;
(2) $result holds information on the
result of executing the query. The information depends on whether the
query gets information from the
database.
a. For queries that do not get any data:
The variable $result contains information on whether the query executed
successfully or not. If it is successful, $result is set to TRUE;
if it is not successful, $result is set to FALSE.
Some queries that do not return
data are INSERT and UPDATE.
b. For queries that return data: The
variable $result contains a result identifier that identifies where the
returned data is
located, not the returned data
itself. Some queries that do return data
are SELECT and SHOW.
(3) mysqli_fetch_assoc ( )
function returns an array called $row with column names in the table of the
database
as keys. For example, row [‘username’],
row[‘password’].
(4) extract ( ) function splits the array $row
into variables that have the same name as the key. For example,
row [‘username’] à $username à $db_name; row[‘password’] à $password à $db_pass.
An alternative version:
$query = "SELECT username AS db_name, password AS db_pass FROM user_info";
$result = @mysqli_query($dbc, $query);
if ($result) {
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_array($result, MYSQLI_ASSOC)) {
if ($fm_username == $row[' db_name '] && SHA1($fm_password) == $row[' db_pass ']) {
echo " <p>Wellcome $username , you are now logged in </p>";
……
mysqli_free_result ( $result ) ; // Free up the resources.
mysqli_close($dbc);
}
}
}
5. Add new data into database
$query = "INSERT INTO customer(first_name, last_name, email, pass, registration_date)
VALUES ('$first_name', '$last_name', '$email', SHA1('$pass'), NOW() )";
$result = @mysqli_query ($dbc, $query); // Execute the query.
if ($result) { // If it ran OK.
echo '<p>Thank you!</p>'; // Print a message:
echo '<p>Your data are registered in the database.</p><p><br /></p>';
}